Having checklist for security is becoming more and more important as you onboard customers. In this article, I will provide a list of security tips to harden Azure AD Environments.
Enable MFA
You should enable MFA for all of your user accounts because a breach of any of those accounts can
lead to a breach of any data that user has access to. MFA is encouraged to be mandatory across all
users, especially in today’s remote workforce. At a minimum, it should be enforced on all global
admins.
Compliance Controls
• CSA CCM301; Control DSI-02
• FedRAMP Moderate; Control IA-3
• GDPR; Control 6.6.5
• ISO 27018:2014; Control C.9.4.2, Control A.10.8
• NIST 800-171; Control 3.5.2
• NIST 800-53; Control IA-3

MFA can be enforced through the following:
- MFA Admin Portal
- Conditional Access Policies
- Security Defaults
Check out my previous article here to learn about the differences between these methods.
Enable MFA for Admins
If you are not going to want to turn MFA on for all users in the organization, you should at least be
turning it on for privileged roles like global admins, exchange admins, etc. Dedicated accounts like
global admin roles should ONLY be used when performing admin task and generally should not be used
for day to day end-user functions. This will help reduce your attack surface from the standpoint of a
privileged account.
Compliance Controls
• CSA CCM301; Control DSI-02
• FedRAMP Moderate; Control IA-3
• GDPR; Control 6.6.5
• ISO 27018:2014; Control C.9.4.2, Control A.10.8
• NIST 800-171; Control 3.5.2
• NIST 800-53; Control IA-3
One of the easiest ways to established MFA for admins is setting up a Conditional access policy and scope the users or groups section to those prviledged roles.
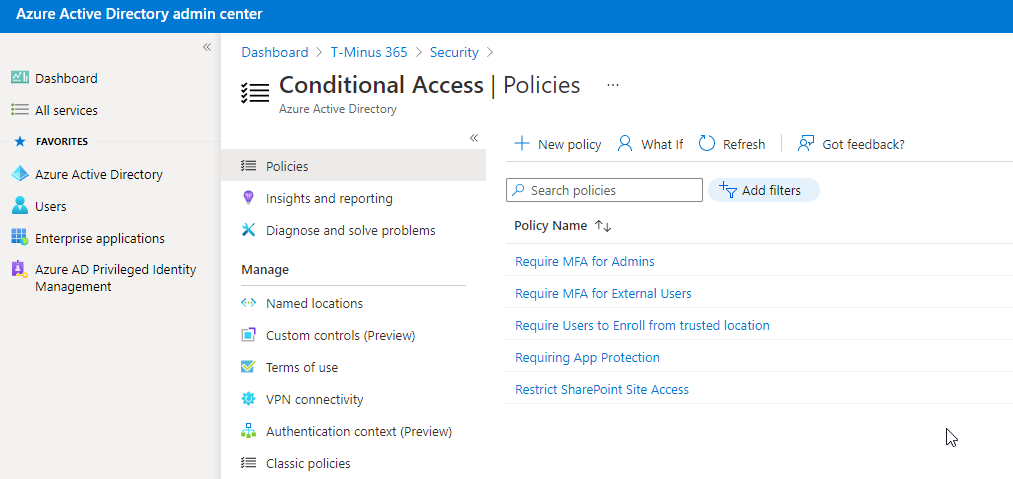
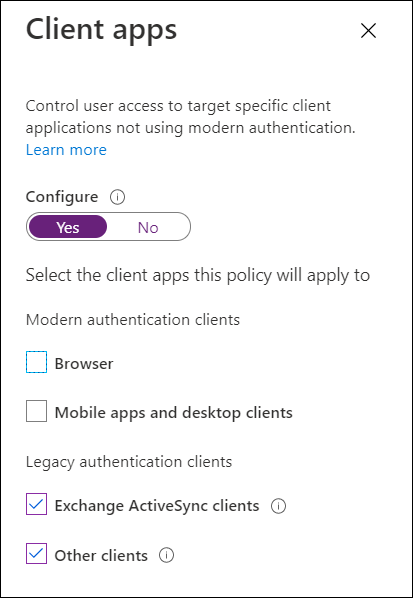
Block Legacy Authentication
End of support for legacy authentication like IMAP/POP is occurred in October of 2020. Legacy
authentication is more susceptible to password spray attacks or brute force attacks because you
cannot layer on MFA. It is advised to block all legacy authentication methods within your customer’s
environments. Legacy authentication can be blocked by enabling Security Defaults or creating a
conditional access policy. Note that if you have any printers/copiers/scanners or IMAP accounts used
for ticketing, you should update those protocols before blocking legacy auth.
Do Not Expire Passwords
Research has found that when periodic password resets are enforced, passwords become less secure.
Users tend to pick a weaker password and vary it slightly for each reset. If a user creates a strong
password (long, complex and without any pragmatic words present) it should remain just as strong in
60 days as it is today. It is Microsoft’s official security position to not expire passwords periodically
without a specific reason. Make sure you have MFA enabled before making this setting change.
Compliance Controls
• FedRAMP Moderate; Control AC-7(a)
• NIST 800-171; Control 3.1.8
• NIST 800-53; Control AC-7(a)
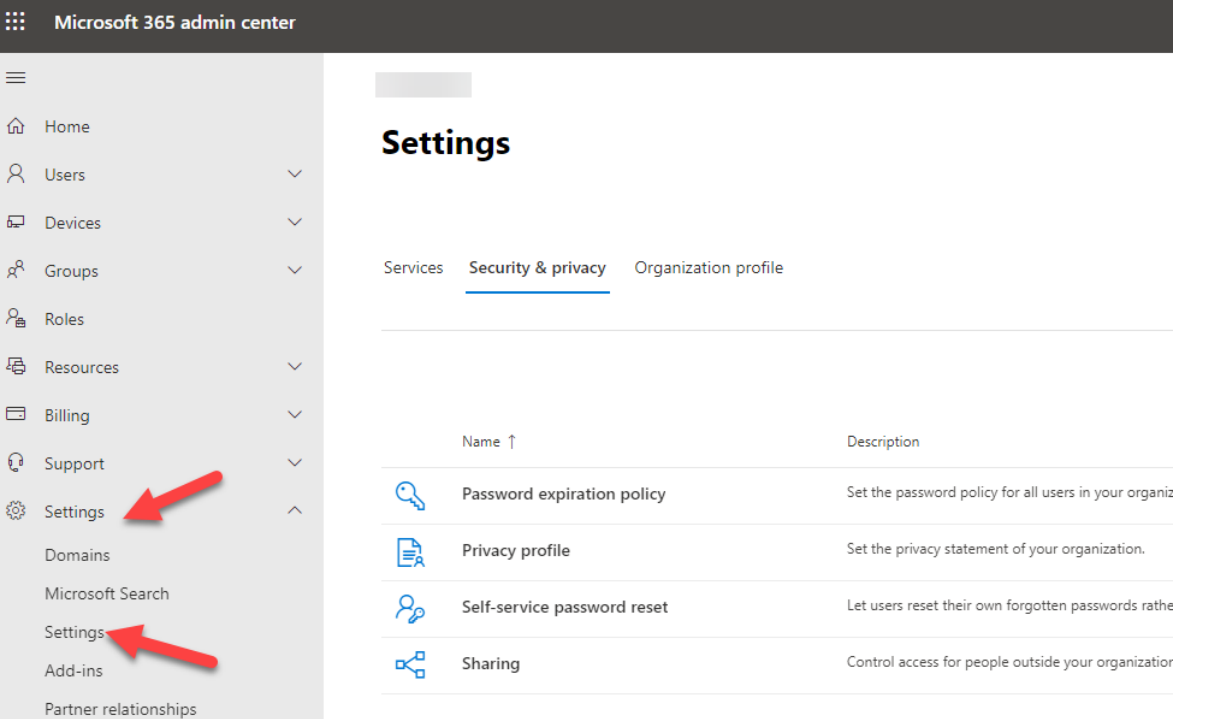
Delete/block accounts not used in last 30 days
Deleting or blocking accounts that haven’t been used in the last 30 days, after checking with owners,
helps prevent unauthorized use of inactive accounts. These accounts can be targets for attackers who
are looking to find ways to access your data without being noticed.
I wrote a script to look up the users who have not logged in for
the last 90 days. Click Here for the script
You can also search in the activity log within Azure AD Admin center to find these users.
Compliance Controls
• FedRAMP Moderate; Control AC-2(3)
• NIST 800-53; Control AC-2(3)
Designate More than 1 Global Admin but fewer than 5
You should designate more than one global tenant administrator because that one admin can perform
malicious activity without the possibility of being discovered by another admin. You could also set this
second admin up with a mailbox in which all of the reports discussed in this playbook are filtered into.
Reducing the number of global admins limits the number of accounts with high privileges that need to
be closely monitored. If any of those accounts are compromised, critical devices and data are open to
attacks. Designating fewer than 5 global admins reduces the attack surface area.
Compliance Controls
• CSA CCM301; Control DSI-02
• FedRAMP Moderate; Control IA-3
• GDPR; Control 6.6.5
• ISO 27018:2014; Control C.9.4.2, Control A.10.8
• NIST 800-171; Control 3.5.2
• NIST 800-53; Control IA-3
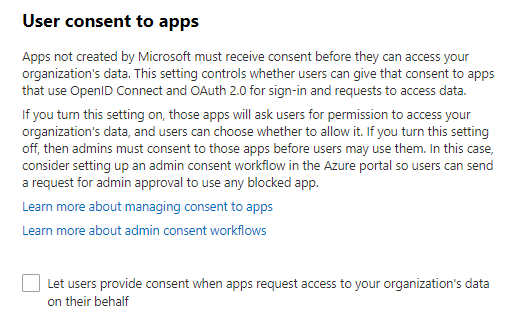
Do not allow users to grant consent to unmanaged applications
Tighten the security of your services by regulating the access of third-party integrated apps. Only allow
access to necessary apps that support robust security controls. Third-party applications are not created
by Microsoft, so there is a possibility they could be used for malicious purposes like exfiltrating data
from your tenancy. Attackers can maintain persistent access to your services through these integrated
apps, without relying on compromised accounts.
Click here for the support article to find this setting
Compliance Controls
• FedRAMP Moderate; Control CM-8(3)(a)
• NIST 800-53; Control CM-8(3)(a)
• NIST CSF; Control ID.AM-1